Venus: Earth's "Evil Twin"
Venus, the second planet from the Sun, is often called Earth's "twin" due to its similar size and mass. However, it's a dramatically different world. Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system, with a surface temperature hot enough to melt lead, due to a runaway greenhouse effect caused by its thick carbon dioxide atmosphere. This dense atmosphere also creates crushing surface pressure. Venus has a slow, retrograde rotation (spinning backward) and is covered in thick clouds of sulfuric acid. While similar to Earth in some ways, Venus's extreme conditions make it a very inhospitable place. Despite this, it's an important planet for studying planetary evolution and the potential for life elsewhere.
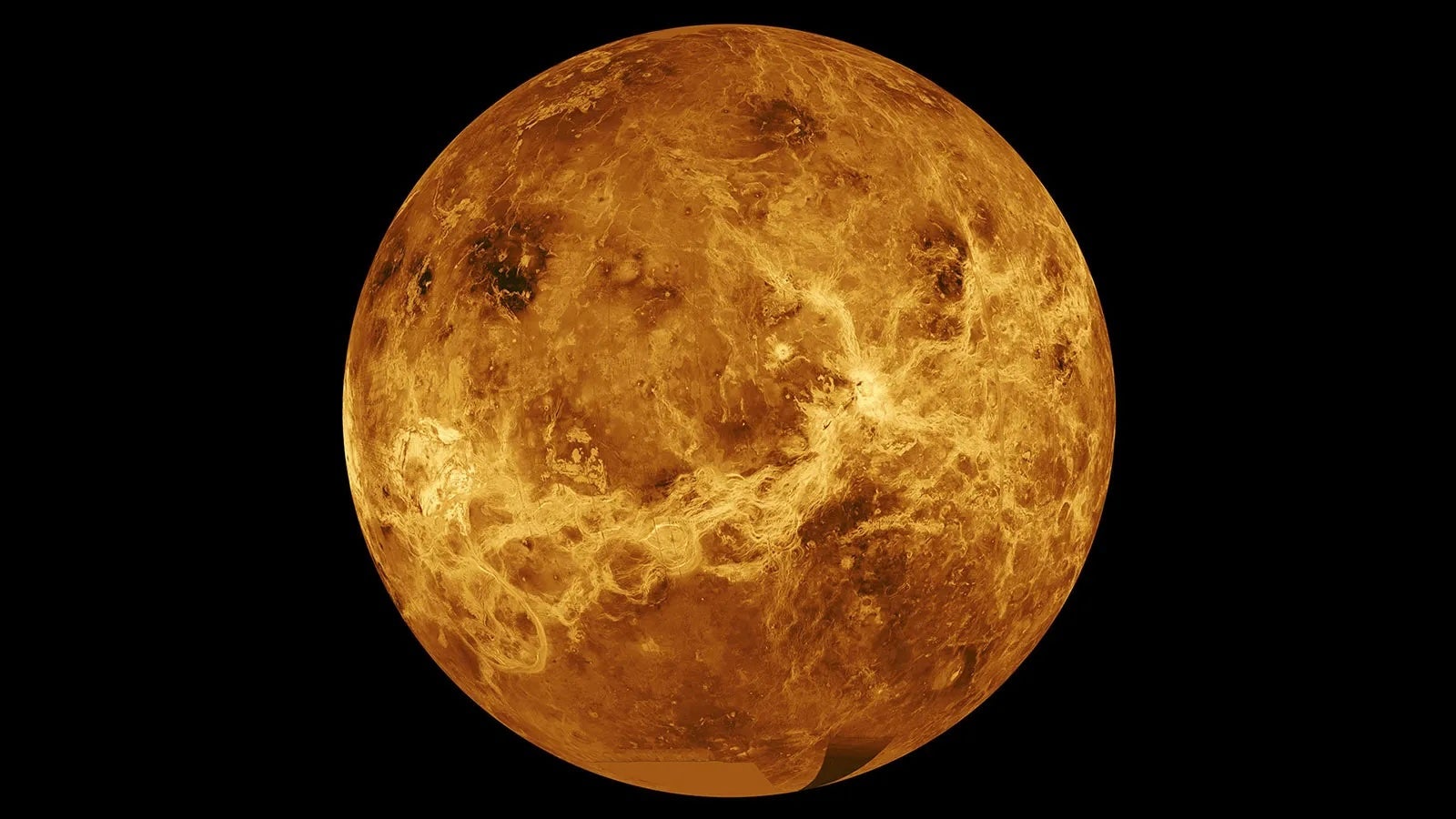

Venus, the second planet from the Sun, is often called Earth's "twin" due to their similar size, mass, and composition. However, this celestial sibling is far from hospitable. Venus is a scorching hot, hellish world, with a thick, toxic atmosphere and a surface hot enough to melt lead. Despite its inhospitable nature, Venus holds a special place in our understanding of planetary evolution and the potential for life beyond Earth.
A Fiery Inferno
Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system, with a mean surface temperature of 464°C (867°F). This extreme heat is due to a runaway greenhouse effect caused by its dense atmosphere, which is 96.5% carbon dioxide. This thick blanket of greenhouse gases traps heat from the Sun, creating a scorching oven-like environment.
The atmospheric pressure on Venus is 90 times that of Earth, equivalent to being 900 meters (3,000 feet) underwater. This immense pressure, combined with the extreme heat and toxic atmosphere, makes Venus a truly hostile place.
A World of Clouds and Volcanoes
Venus is perpetually shrouded in thick clouds of sulfuric acid, which reflect sunlight and make the planet appear bright in the night sky. These clouds also contribute to the greenhouse effect, trapping heat and further raising the planet's temperature.
Beneath the clouds, Venus has a diverse terrain, with mountains, canyons, and volcanoes. The planet's surface is relatively young, geologically speaking, suggesting recent volcanic activity. Venus has more volcanoes than any other planet in our solar system.
A Slow Rotation and Retrograde Motion
Venus has an unusually slow rotation, taking 243 Earth days to complete one rotation. This means that a day on Venus is longer than its year, which takes 225 Earth days.
Venus also rotates in a retrograde direction, meaning it spins clockwise, opposite to most other planets in our solar system. The reason for this unusual rotation is not fully understood, but it may be due to a collision with a large object in the early solar system.
Exploration of Venus
Despite its harsh conditions, Venus has been visited by numerous spacecraft over the years. The first spacecraft to reach Venus was the Soviet Venera 4 in 1967. Since then, several other missions have explored the planet, including NASA's Magellan, which mapped the surface of Venus using radar.
These missions have provided valuable insights into the planet's atmosphere, geology, and history. However, much remains unknown about Venus, and future missions are planned to further explore this fascinating world.
The Mystery of Venus's Past
One of the biggest mysteries surrounding Venus is its past. Scientists believe that Venus may have once been a much more Earth-like planet, with liquid water oceans and a more temperate climate. However, something happened to transform Venus into the scorching hot world we see today.
Understanding what happened to Venus is crucial for understanding the evolution of planets and the potential for life beyond Earth. By studying Venus, we can learn more about the factors that make a planet habitable and the conditions that can lead to a planet becoming uninhabitable.
Venus: A Cautionary Tale
Venus serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of a runaway greenhouse effect. The planet's extreme heat and toxic atmosphere are a stark reminder of the potential consequences of climate change.
By studying Venus, we can learn more about the delicate balance of Earth's climate system and the importance of taking action to prevent runaway global warming.
The Future of Venus Exploration
Despite its challenges, Venus remains a prime target for future exploration. Several missions are planned to study the planet in more detail, including NASA's VERITAS and DAVINCI missions.
These missions will use advanced technologies to map the surface of Venus, analyze its atmosphere, and study its geological history. By exploring Venus, we can gain a deeper understanding of our solar system and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Conclusion
Venus is a fascinating and enigmatic planet, full of mysteries and surprises. Despite its harsh conditions, Venus holds a special place in our understanding of planetary evolution and the potential for life beyond Earth. By continuing to explore Venus, we can learn more about our solar system and the factors that make a planet habitable.
What's Your Reaction?
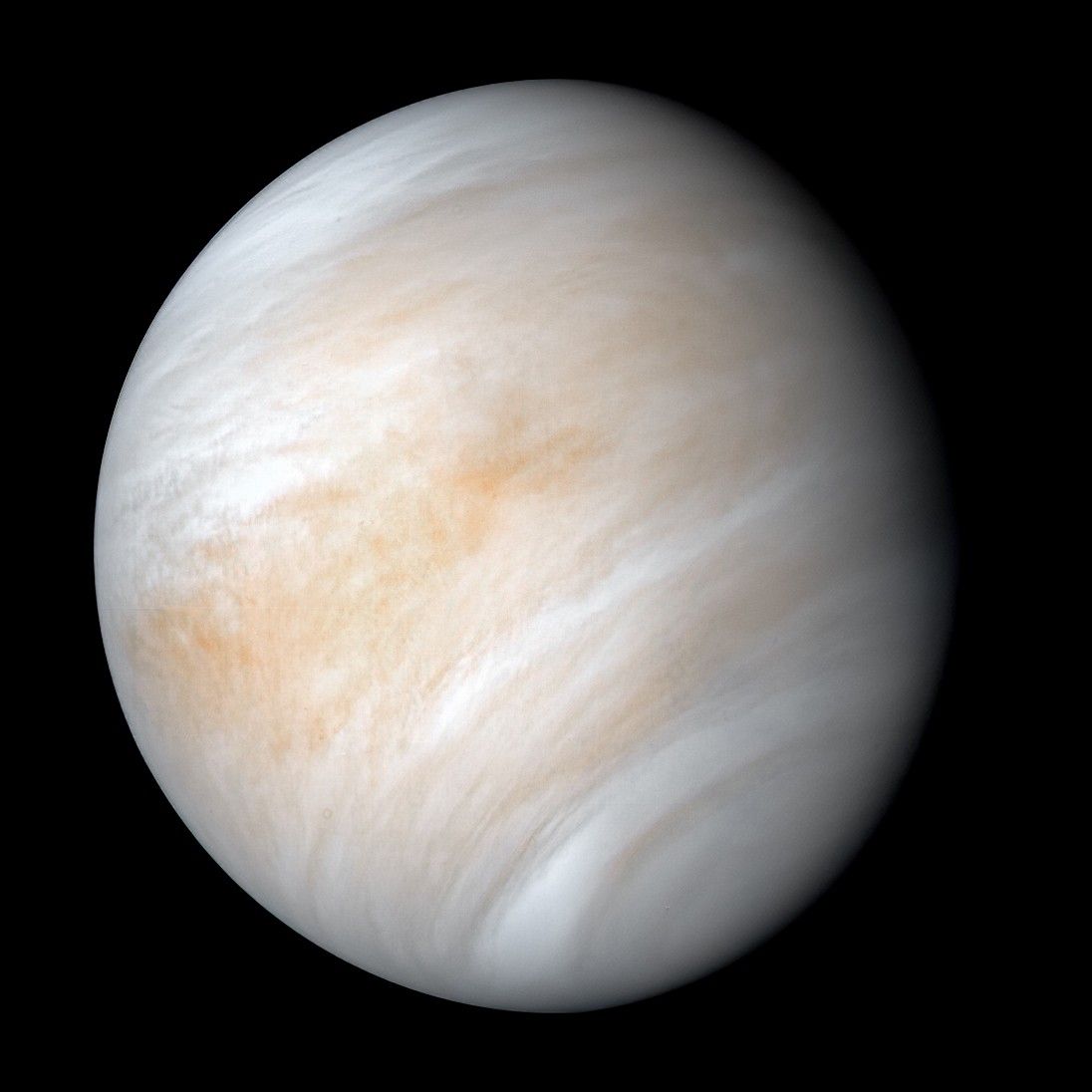












/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/54/66/546650fa-26a4-40fd-8d6d-5a7a04540f81/rosetta2.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(999x0:1001x2)/robert-prevost-050825-1-39395418ab494da5a3a700c9478e66c8.jpg)














































format(webp))
format(webp))

























