NASA Sheds Light on Neptune: New Discoveries Reveal Mysteries of the Distant Ice Giant
Explore the mysteries of Neptune, the distant ice giant of our solar system, known for its deep blue hue, extreme weather, and powerful winds. Learn about recent scientific discoveries and why astronomers are eager for a dedicated mission to this fascinating planet.
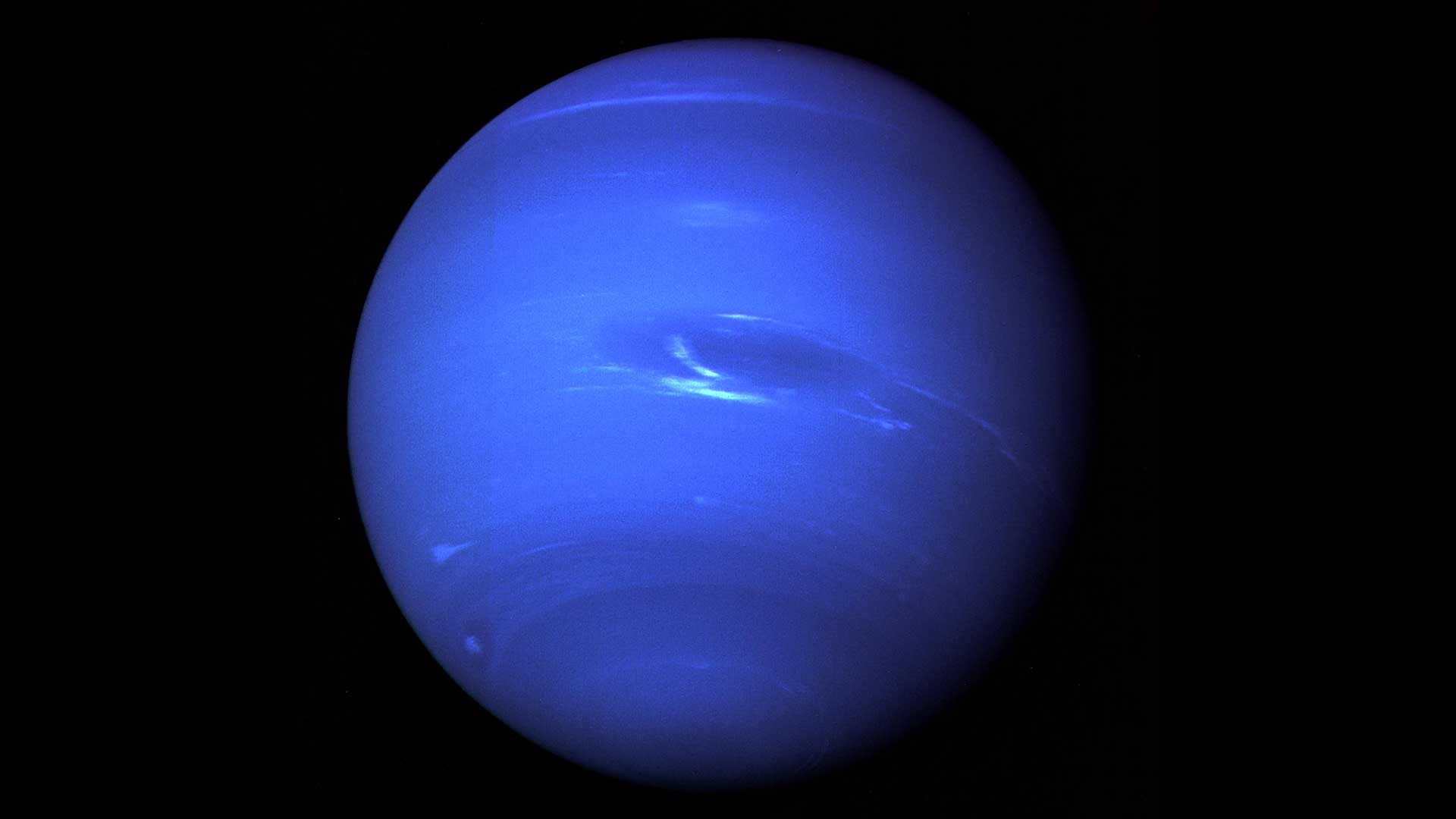

Neptune, the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in our solar system, continues to fascinate astronomers with its mysterious atmosphere, dynamic weather systems, and unique internal structure. Often called an "ice giant," Neptune stands out due to its deep blue color, powerful storms, and extreme weather, including the fastest winds recorded in the solar system.
Discovered in 1846 by Johann Galle based on predictions by French mathematician Urbain Le Verrier, Neptune was the first planet located using mathematics before visual confirmation. It is roughly four times wider than Earth and primarily composed of hydrogen, helium, and ices like water, ammonia, and methane. Its striking blue color comes from methane in its upper atmosphere, which absorbs red light and reflects blue.
Recent observations by NASA and other space agencies have provided fresh insights into Neptune’s turbulent atmosphere and evolving climate. Using the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories, scientists have monitored massive storms on Neptune, including dark spots similar to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. These anticyclonic storms, which appear and disappear over a few years, are key to understanding the dynamics of Neptune’s atmosphere.
One of the most surprising features of Neptune is its extreme wind speeds, which can exceed 2,100 kilometers per hour (1,300 miles per hour). These are the fastest sustained winds recorded on any planet in the solar system. Scientists are still trying to understand what drives such extreme atmospheric activity in a planet that receives only a tiny fraction of the sunlight Earth does.
Neptune’s weather is also influenced by its internal heat. The planet emits more than twice as much energy as it receives from the Sun, indicating a hot interior. This heat drives convection currents in the atmosphere, fueling storms and high-speed winds. The source of this internal heat remains a subject of scientific investigation.
Neptune also has a faint and fragmented ring system, which was first confirmed by Voyager 2 during its flyby in 1989. Voyager 2 remains the only spacecraft to have visited Neptune directly. The planet has 14 known moons, the largest being Triton, which is geologically active and orbits in the opposite direction of Neptune’s rotation—suggesting it may have been captured from the Kuiper Belt.
While no new mission to Neptune is currently underway, astronomers and planetary scientists continue to advocate for a dedicated probe. A Neptune orbiter could reveal critical details about its interior, magnetosphere, moons, and atmospheric composition—information that could also apply to exoplanets similar in size and makeup.
With advances in telescopic technology and increasing interest in the outer planets, Neptune is once again in the spotlight. As scientists push the boundaries of what we know about the outer solar system, Neptune remains one of the most intriguing and least explored worlds—a blue giant filled with secrets waiting to be uncovered.
What's Your Reaction?











/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/54/66/546650fa-26a4-40fd-8d6d-5a7a04540f81/rosetta2.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(999x0:1001x2)/robert-prevost-050825-1-39395418ab494da5a3a700c9478e66c8.jpg)














































format(webp))
format(webp))


























